Electrical Earthing: Ensuring Safety and Protection
Electrical earthing plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and protection of electrical systems and equipment. It involves the process of transferring immediate discharge of electrical energy directly to the earth, using a low resistance wire. By connecting the non-current carrying part of the equipment or the neutral of the supply system to the ground, electrical earthing helps prevent damage and ensures the smooth functioning of electrical installations.
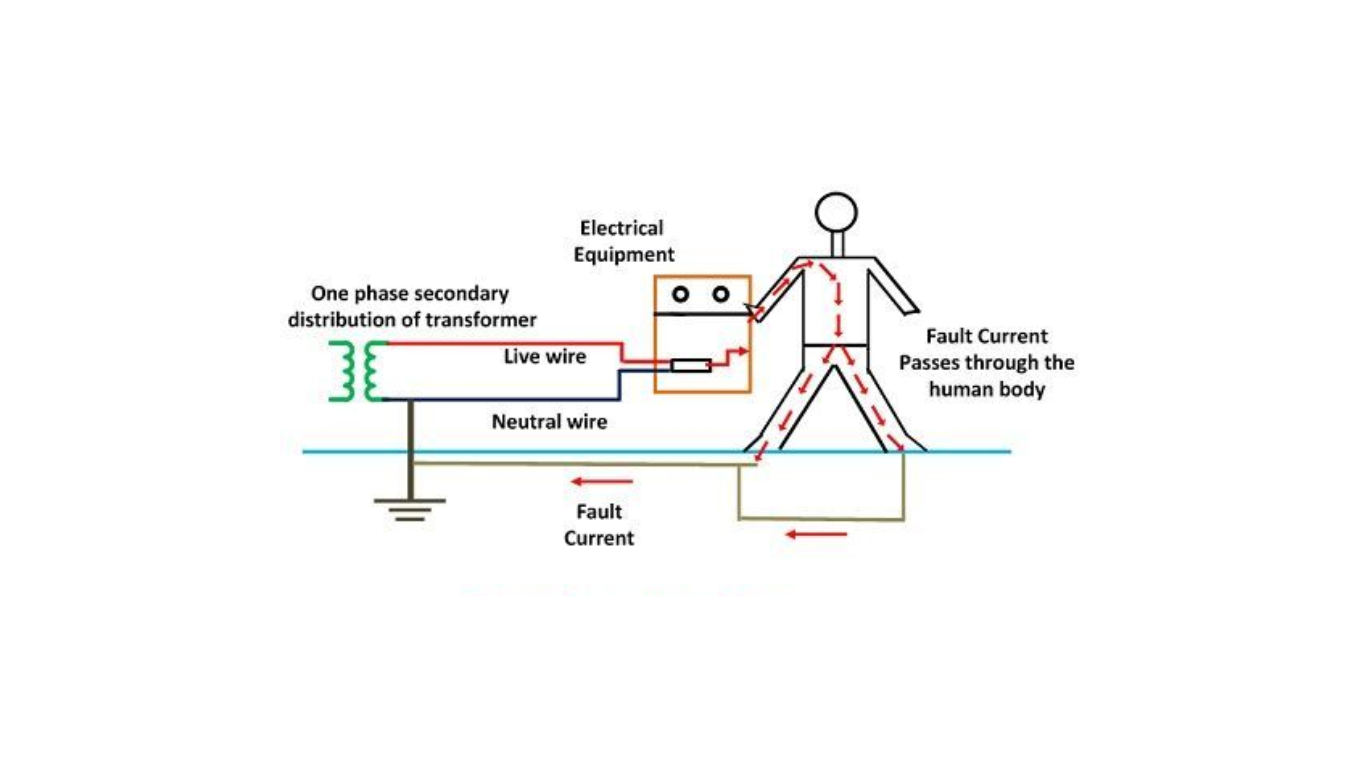
Types of Electrical Earthing
There are two main types of electrical earthing:
1. Neutral Earthing
Neutral earthing, also known as system earthing, involves directly connecting the neutral of the system to the earth using a galvanized iron (GI) wire. This type of earthing is commonly provided to systems with star winding, such as generators, transformers, and motors. Neutral earthing ensures a safe and reliable electrical system by diverting any fault current to the earth.
2. Equipment Earthing
Equipment earthing focuses on providing earthing to individual electrical equipment. The non-current carrying part of the equipment, such as its metallic frame, is connected to the earth using a conducting wire. In case of a fault in the equipment, the short-circuit current is directed to the earth via the wire, effectively protecting the system from potential damage.
Importance of Electrical Earthing
Electrical earthing is crucial for several reasons:
- Personnel Safety: Earthing protects individuals from the dangers of short-circuit currents, ensuring their safety in electrical installations.
- Continuity of Operation: Even in the event of insulation failure, earthing provides the easiest path for the flow of short-circuit currents, maintaining continuity of operation.
- Protection from Surges and Lightning Discharge: Electrical earthing safeguards both the equipment and personnel from high voltage surges and lightning discharges, preventing damage and ensuring safety.
Implementing Electrical Earthing
To achieve proper earthing, the respective parts of the installation need to be electrically connected to a system of conductors or electrodes placed near or below the ground level. An earthing mat or electrode is positioned below ground level, featuring a flat iron riser. This riser connects all the non-current carrying metallic parts of the equipment.
During a fault, the fault current from the equipment flows through the earthing system to the earth, effectively protecting the equipment. The earth mat conductors rise to a voltage equal to the resistance of the earth mat multiplied by a ground fault.
The assembly responsible for the electrical connection is known as the earthing, while the metallic conductors connecting the installation parts to the earthing are called electrical connections. Together, they form the earthing system, ensuring the safe operation of electrical installations.
In conclusion, electrical earthing is a critical aspect of electrical systems, providing safety, protection, and continuity of operation. By understanding the different types of earthing and its importance, we can ensure the reliable and secure functioning of electrical installations.